Reiffel - Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke: Epidemiology - Figure 3
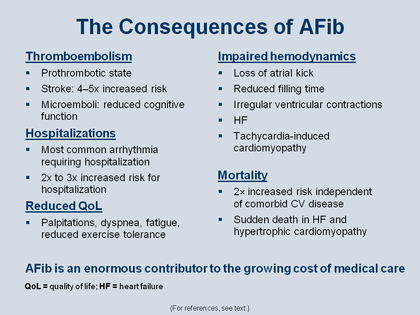
The Consequences of AFib
AFib has a number of significant consequences, including increased risk for thromboembolism, impaired hemodynamics, hospitalizations, reduced quality of life, and mortality; in addition, for patients it results in the symptoms that relate to all of those and is an enormous contributor to the growing cost of medical care [4] [5] [6] [7] Of these consequences, this presentation will focus largely on thromboembolism. Thromboembolism is the result of a prothrombotic state that develops in the atria in some patients with AFib; in patients with certain structural disorders the risk of stroke is increased 4–5-fold. Thromboembolism can also result in microemboli, which can lead to reduced cognitive function.
Reiffel JA. Am J Med 2013; 126: 00-00.